
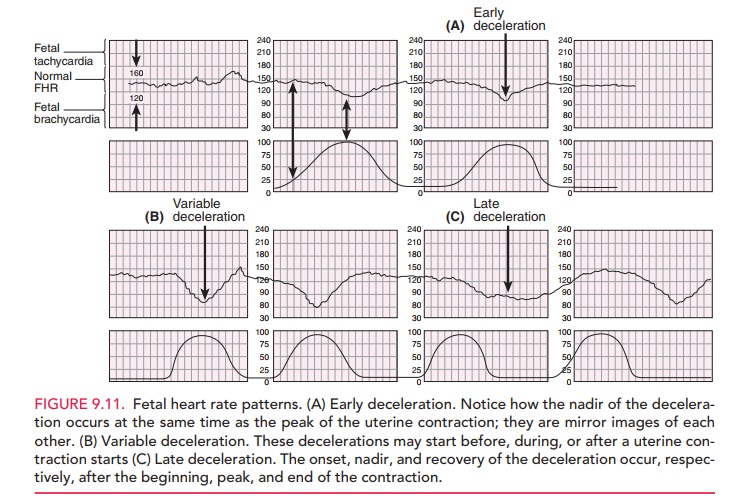
It may also be used to help differentiate true versus false labor. Outside of the immediate intrapartum period, fetal monitoring may be used to evaluate for placental abruption, commonly when an obstetric patient presents following abdominal trauma. However, no benefit has been demonstrated from the use of fetal monitoring in most other perinatal outcomes, including Apgar scores, the incidence of neurologic injury, cerebral palsy, developmental delay, and NICU admission. Įvidence is mixed on the effect of FHR monitoring on neonatal mortality, and a small reduction in the incidence of neonatal seizures has been observed when fetal monitoring is used. However, the evidence basis for this is controversial as research has demonstrated that routine FHR monitoring is associated with increases in the rates of both operative vaginal deliveries and Cesarean sections without significantly improving most newborn or childhood outcomes. In many areas of the United States, continuous intrapartum fetal monitoring has been used routinely for most women undergoing labor and delivery. This is intended to benefit the mother and fetus by providing obstetric clinicians with additional real-time information that they may use to determine if any intervention is necessary. The relationship between these two variables is widely accepted to correlate with the oxygenation status of the fetus. Summarize how interprofessional can improve diagnostic results when patients require a fetal heart tracing.Ĭontinuous fetal monitoring, or cardiotocography, is a method of tracking the fetal heart rate (FHR) along with the occurrence of uterine contractions.Identify the pathophysiology of fetal heart tracings.Describe the fetal heart patterns on the tracing.Review specific fetal heart tracings associated with a certain pathology.It will highlight the role of the interprofessional care team in implementing and interpreting its results. This activity reviews the methods for fetal monitoring as well as its indications and physiologic basis. Less than that is transient cord compression is not worrisome.Intrapartum fetal monitoring is commonly performed in labor on the basis that changes in the fetal heart rate pattern may correlate with the fetal oxygenation status, thereby providing additional information to obstetric clinicians who must decide whether or not any intervention is necessary. If it lasts more than 60 seconds it is considered severe prolonged cord compression. Variable = abrupt decrease in FHR that’s variable in relation to contractions. Caused by uteroplacental insufficiency and fetal hypoxia. Late = Gradual decrease in FHR nadir of which is delayed till after the onset of contraction. Prolonged acceleration = acceleration length of ≥ 2 mins but < 10 mins.Ĭause: uterine contractions, fetal movement and scalp stimulation this is always reassuring!ĭeceleration = decrease in FHR associated with uterine contractions.Įarly = Gradual decrease in FHR nadir of which coincides with contraction peak (mirrors contractions). Marked = > 25 bpm change from the baseline.Īcceleration = abrupt increase in FHR which is 32 weeks.įrom onset to return to peak, accelerations take no more than 10-15 sec. Moderate = 6 – 25 bpm change from baseline. beta agonists, atropine, cocaine), maternal hyperthyroidism, placental abruption.įetal tachycardia = FHR baseline treat acidosis. MATERNAL (infection, fever, medications (e.g. If a total of 2 mins (12 boxes) of baseline can’t be seen -> baseline is indeterminate.Ĭhanges in baseline = acceleration or deceleration length of ≥ 10 mins.įetal tachycardia = FHR baseline > 160 bpm for at least 10 mins.įETAL (repetitive decelerations, fetal tachyarrhythmia, prematurity). ĭon’t include accelerations, decelerations, & marked variabilities (>25 bpm)Įach box horizontally on CTG = 10 seconds, meaning each 6 boxes = 1 minute. The length of recorded fetal heart rate (FHR) taken is usually 10 minutes (the minimum baseline can be as short as 2 minutes).ĬTG is reviewed in relation to mom’s contractions when in labor.ĬTG can be used to monitor FHR during antenatal care from 28 weeks gestation.įHR Baseline = a total of at least 2 min of FHR being around the level of a certain bpm + variabilities. Cardiotocography (CTG) = Non-stress test (NST).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
